General Accounting
Accounting is the function of organizing the financial data in the business. In essence, the flow of money in the business is recorded, tracked, and monitored by the Shop Owner’s Accounting. In this case, the Shop Owner will often have to monitor their revenues and expenses. Using the Content Management System will allow tracking, recording, and monitoring the flow of money in the Shop while the Shop Owner manage Orders and Supplies.
Discussed below are some important points that the Shop Owner need to keep in mind for day-to-day business:
Set and Update Product Stock
The Shop Owner needs to check their Current Product Stock to ensure that they can fulfill the Customers’ Orders in time. For convenience, the Stock Count, Stock for Sale, and Low Stock Threshold can be set during the Product creation which will automatically provide reminders of low stock, out of stock, and available Product stock.
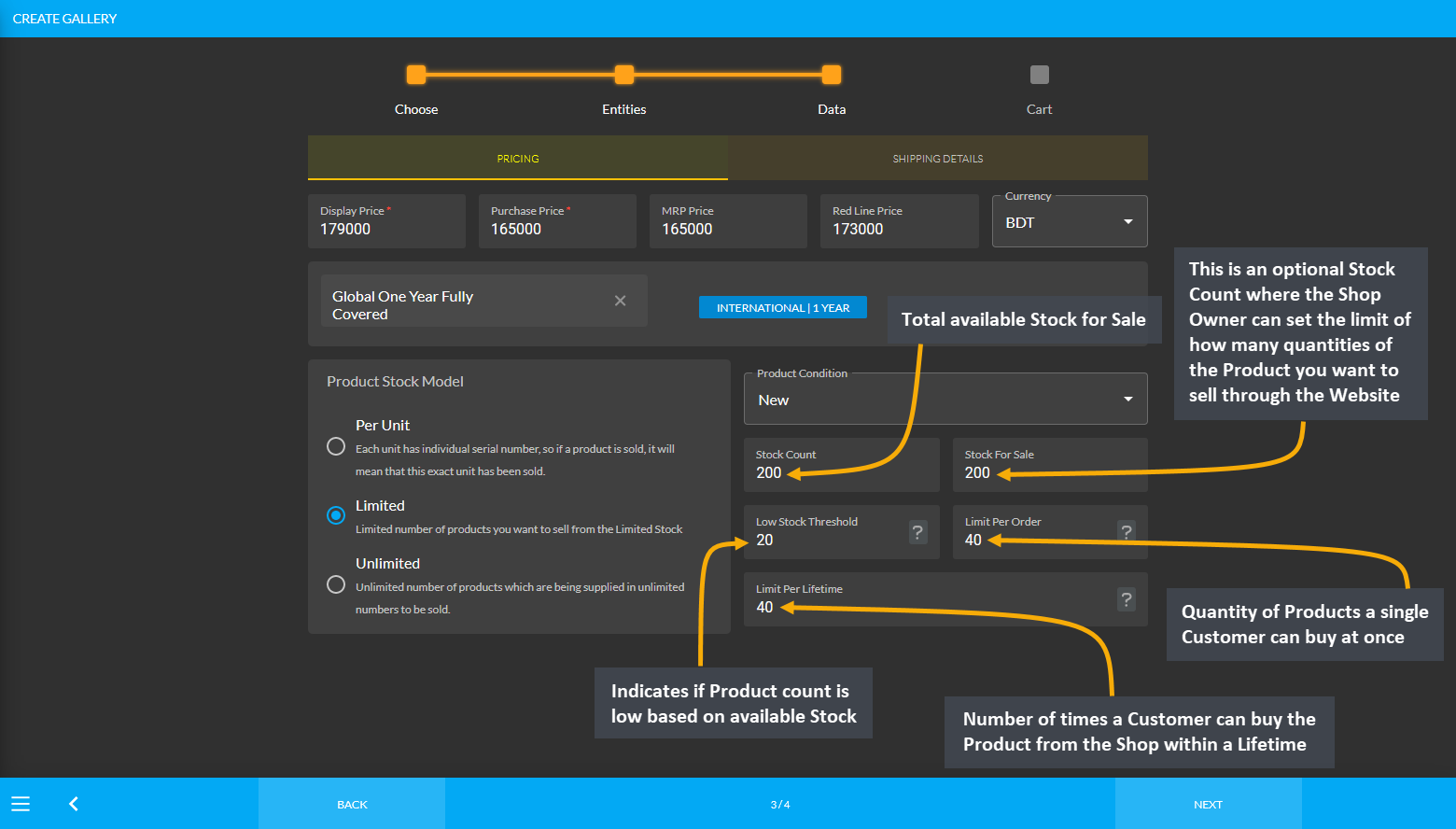
Image 1: Stock Count, Stock for Sale, and Low Stock Threshold can be set during the Product creation.
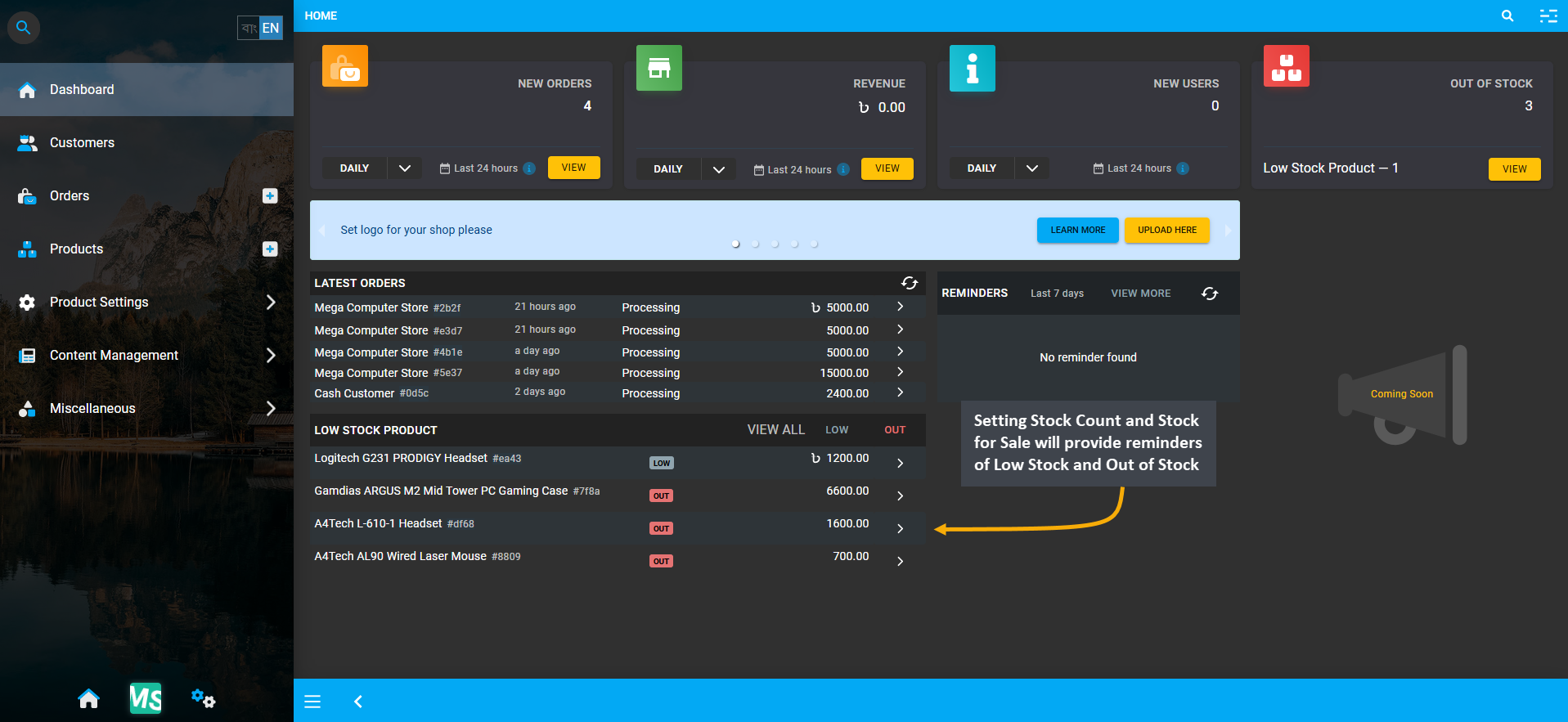
Image 2: Setting Stock Count and Stock for Sale will provide reminders of Low Stock and Out of Stock.
Set Product Prices
The Shop Owner needs to set their Product prices and check them often with the market prices to make sure that the Product Prices are set higher than expenses for making profit. They can use strategic pricing methods, like initially setting low Product prices and raising the Product prices once they have enough Customers, or setting high initial prices and reducing them over time, or discount pricing by regularly marking down goods or services.
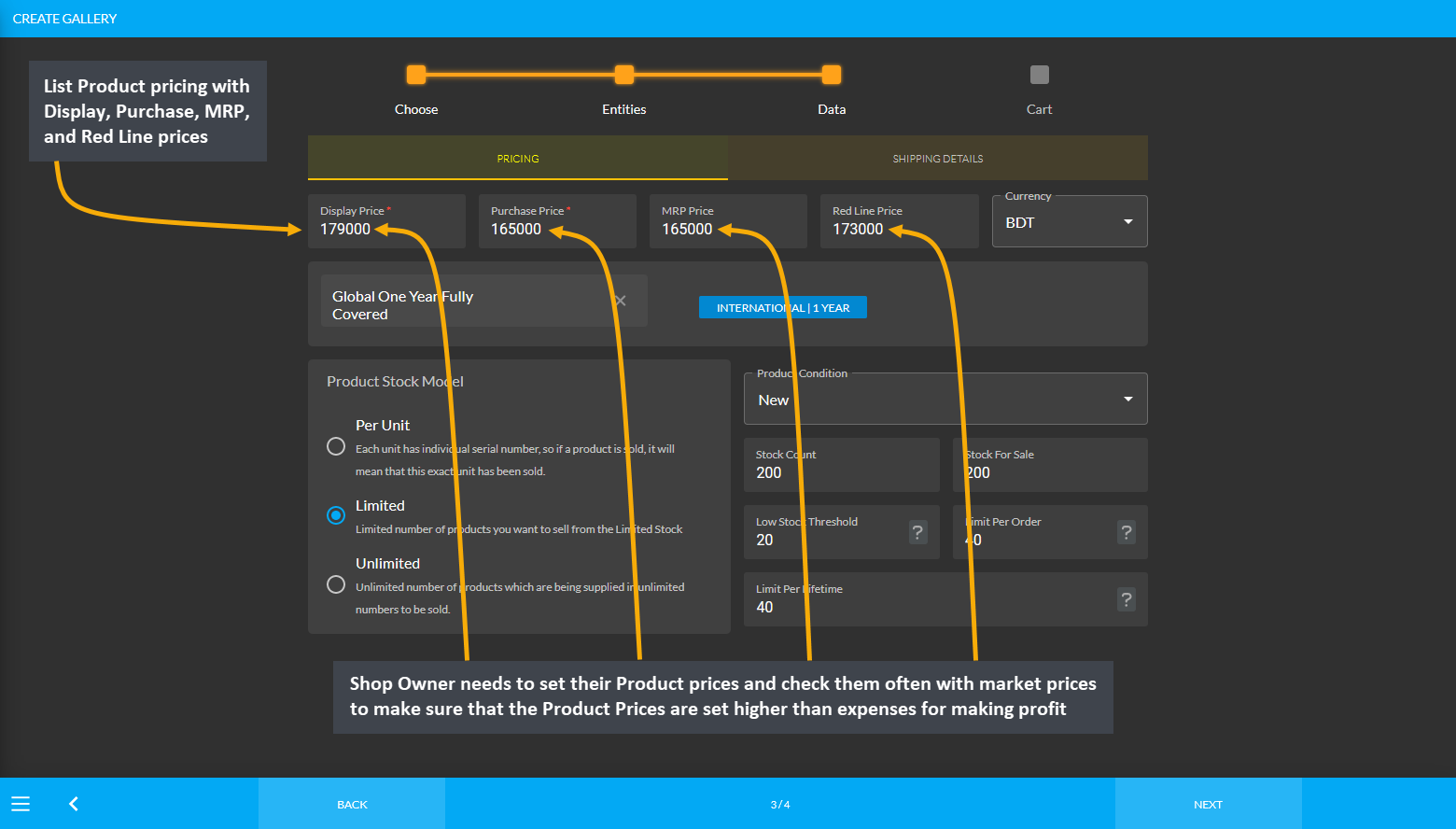
Image 3: Shop Owner needs to set the various Product prices and check them often with the market prices.
Record of Product Purchase
The Shop Owner purchasing Product Batches from the Supplier will be recorded on Unit Stock Management page. Therefore, when the Shop Owner purchases Products from Suppliers, they can set Payment Method to pay for purchase from the Supplier on Add Product Stock page. The record of purchase by the Shop Owner from the Supplier will be available for view under the Ledger Breakdown page, which can be printed for keeping record.
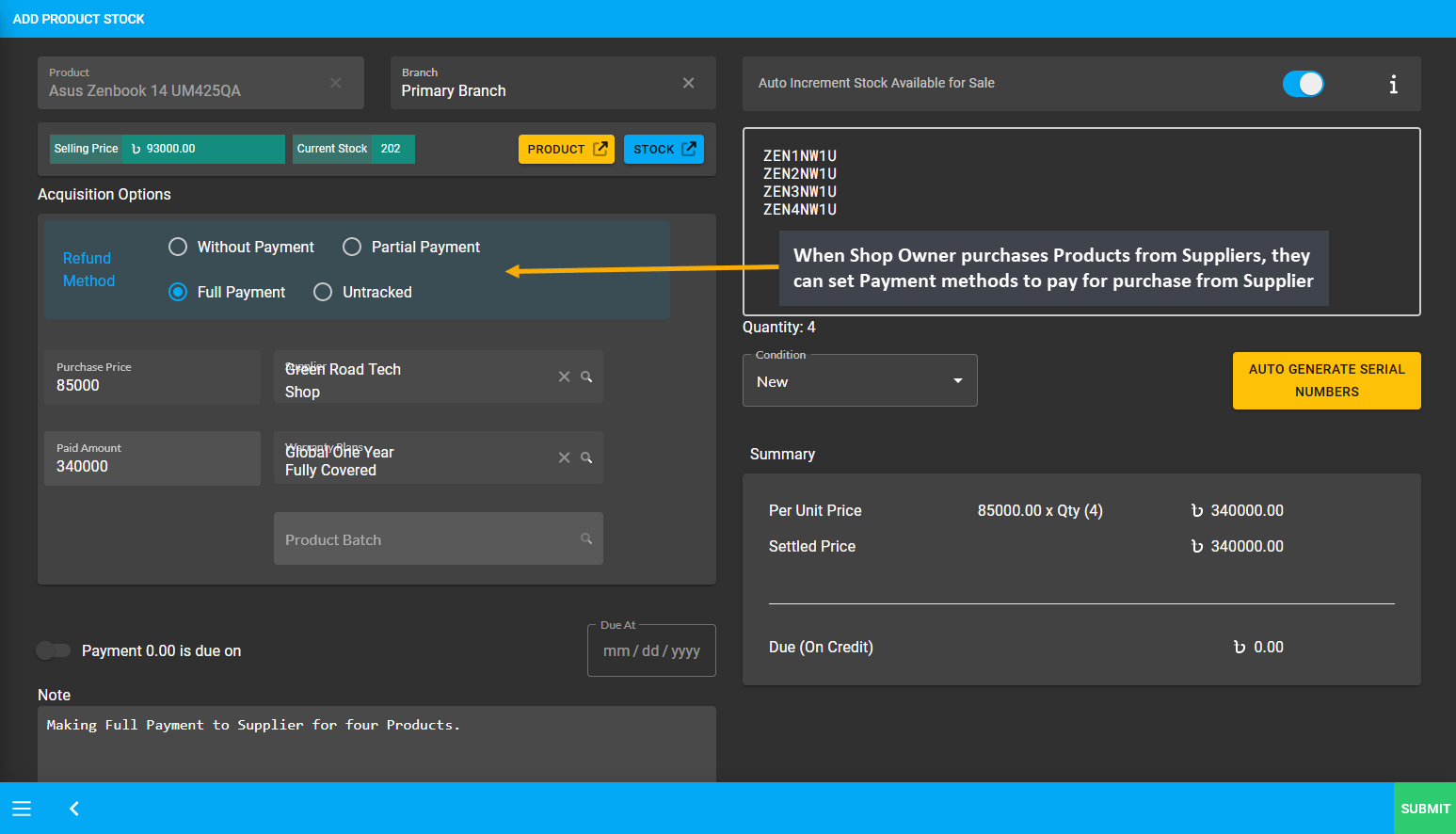
Image 4: When Shop Owner purchases Products from Suppliers, they can set their preferred Payment Method.
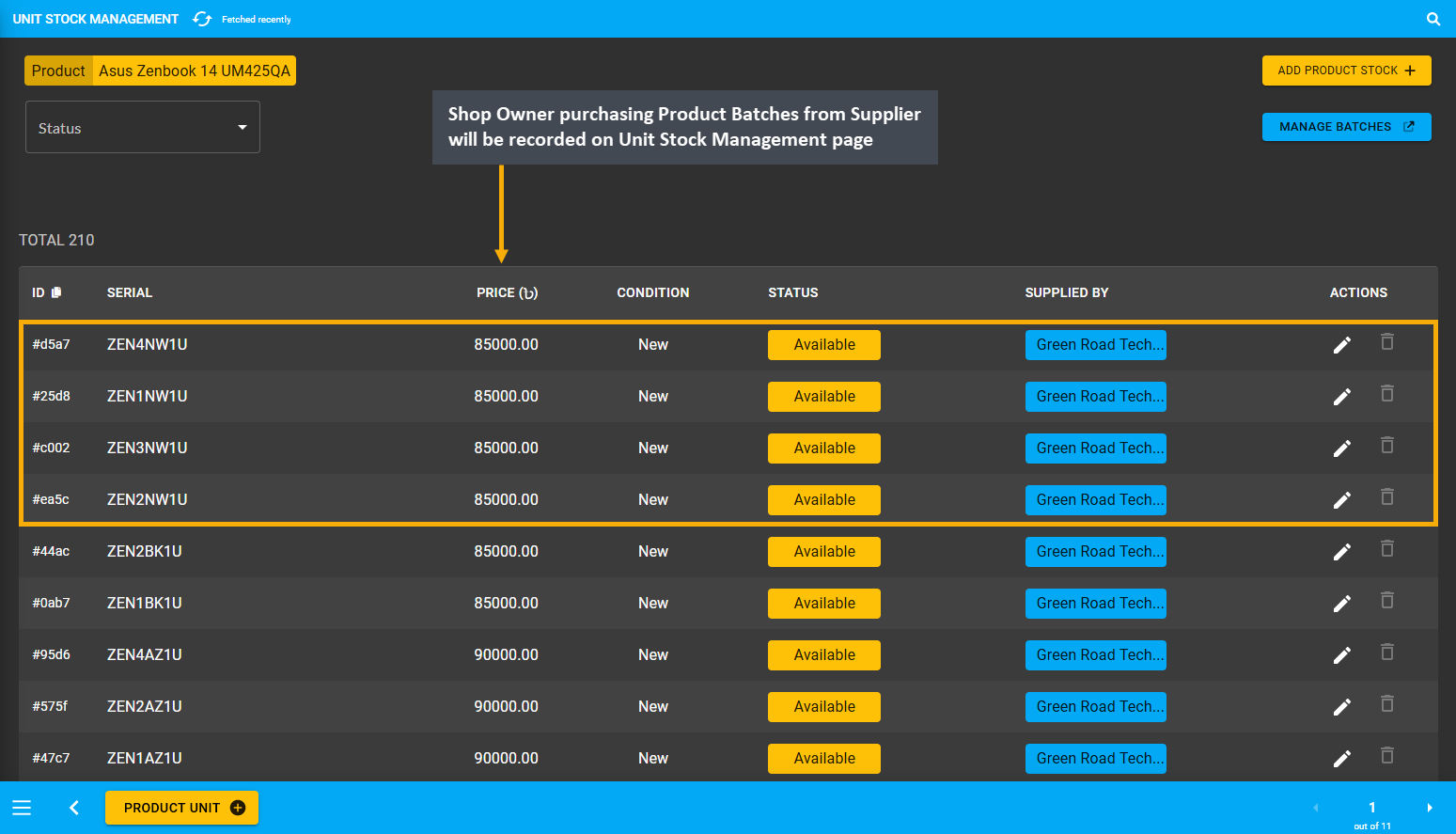
Image 5: Shop Owner purchasing Products from Supplier will be recorded on the Unit Stock Management page.
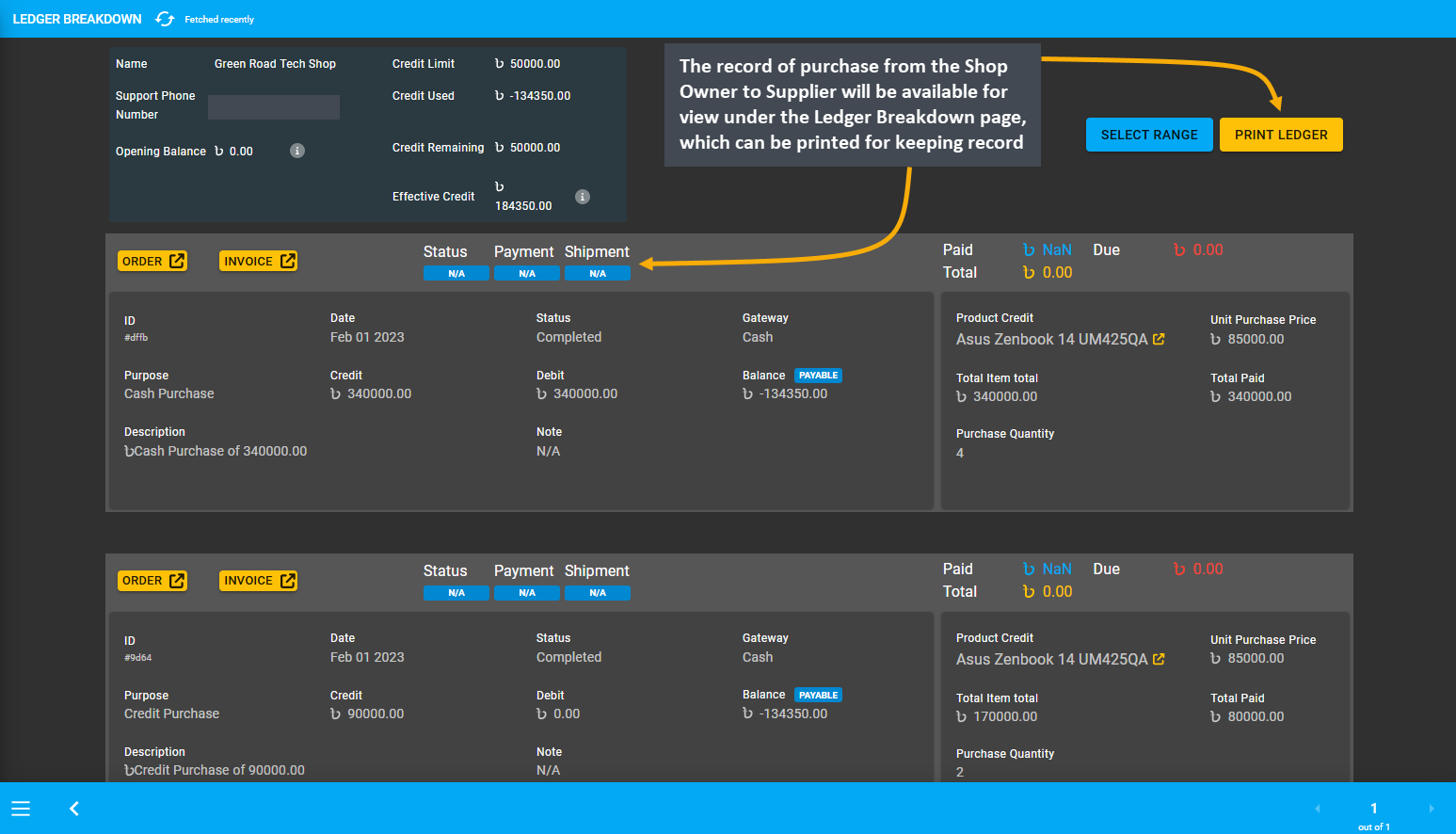
Image 6: Record of purchase by Shop Owner from Supplier will be recorded on the Ledger Breakdown page.
On a similar note, if the Shop Owner sell Products to Customers without demanding immediate payment, then they need to create invoices. Create invoices with information like the date of transaction, Customer, Seller, and Product information, the due amount, payment terms, and an invoice number for reference to keep record.
Sales Record with Cost Basis Report
Shop Owner needs to keep track of their Product sales on a day to day basis. Maintaining a record on paper or electronic is important for any business. The sales record can be organized from invoices, sales receipts, cash register, VAT documents, and bank statements. So, record every sale and amount charged to Customers.
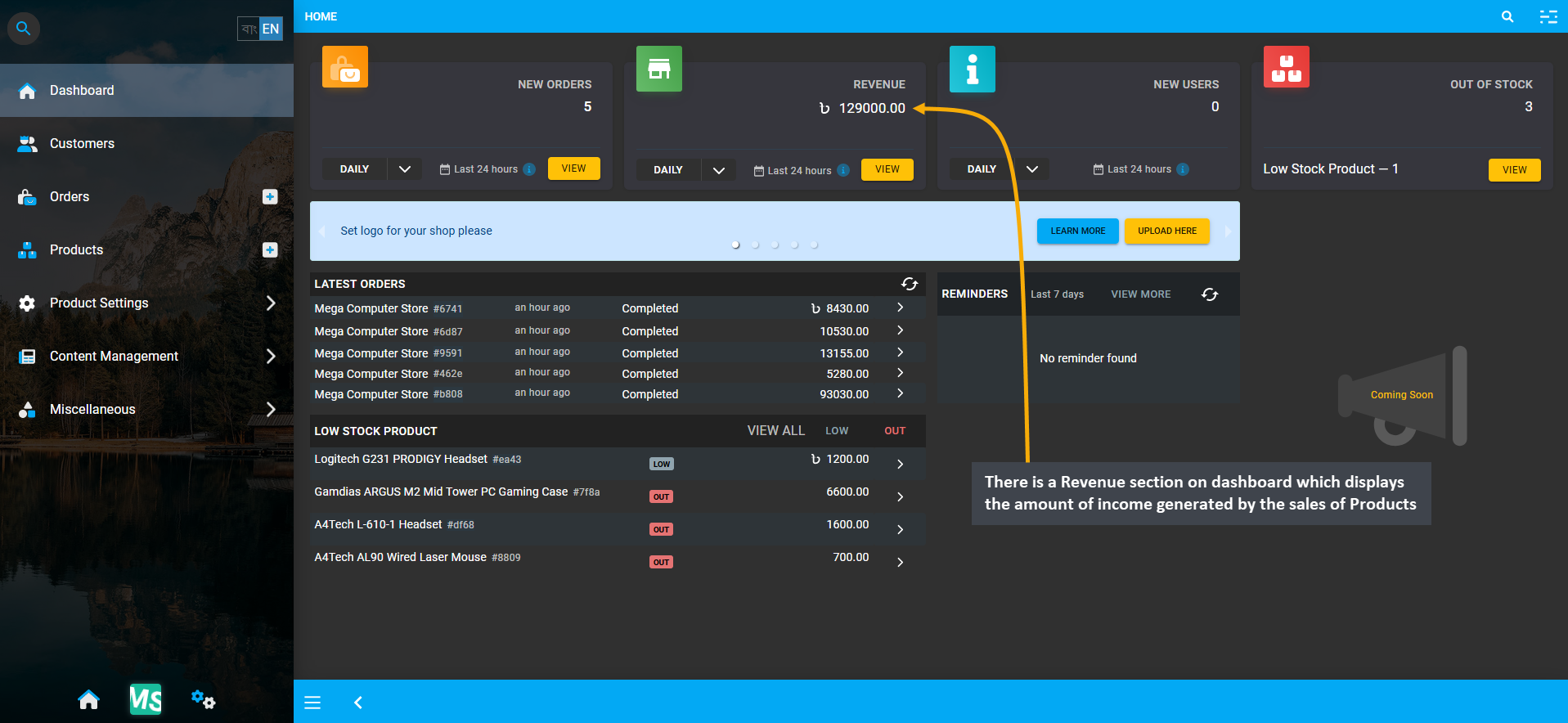
Image 7: Revenue section on dashboard displays the amount of income generated by the sales of Products.
To observe the progress, the Cost Basis Report of daily, weekly, monthly, or yearly sales is automatically updated by the CMS. There is also a Revenue section on dashboard which displays the amount of income generated by the sales of Products. Since recording daily profit and loss is one of the fundamental financial documents, the Shop Owner needs to keep track of how much money their business brings and how much are their expenses.
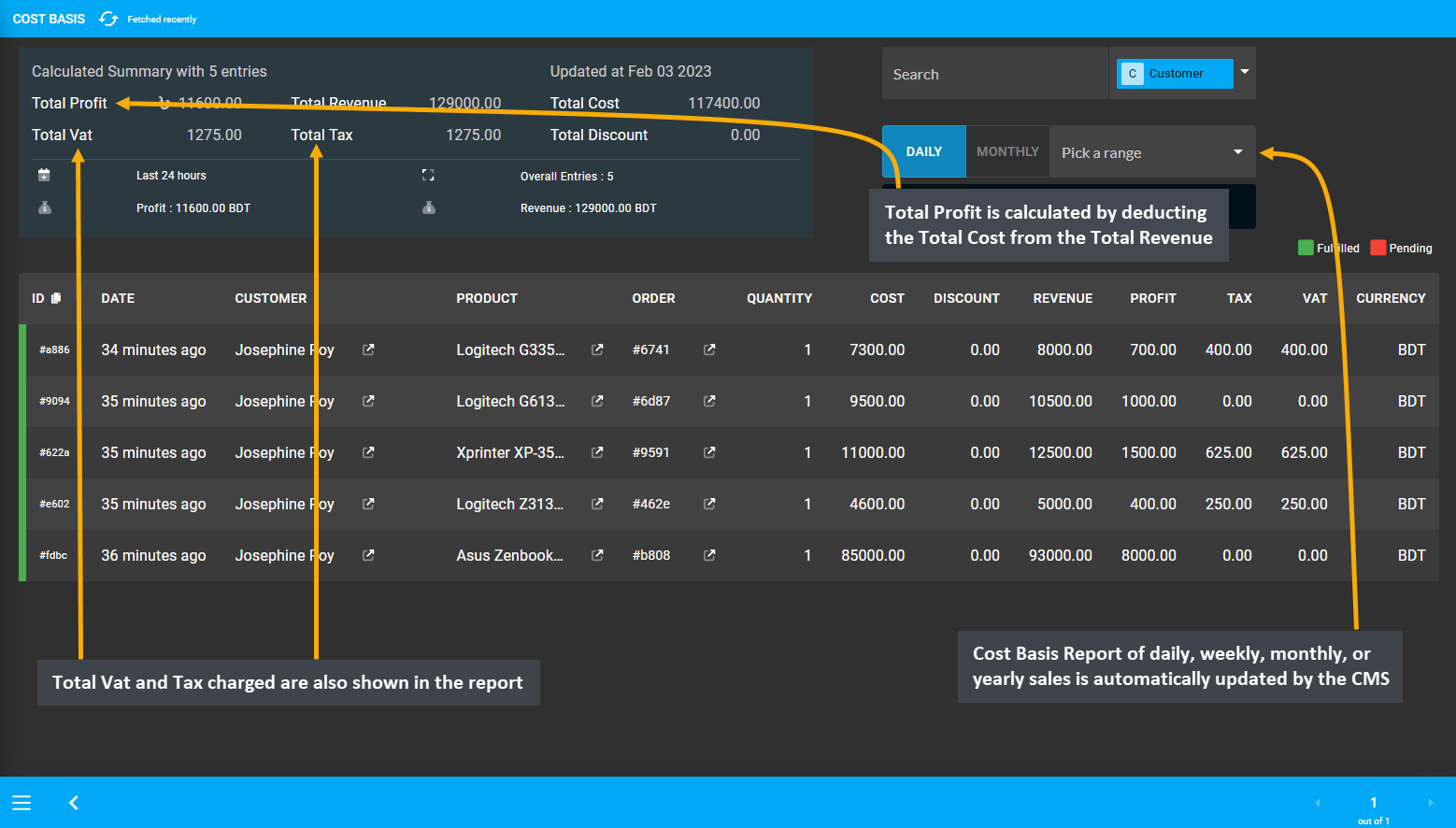
Image 8: Cost Basis Report of daily, weekly, monthly, or yearly sales is automatically updated by the CMS.
Therefore, it is important to determine the cost of Products sold and to keep track of revenue earned from selling the Products which are available through the automated Cost Basis Report. Total Profit is calculated by deducting the Total Cost from the Total Revenue. Total Vat and Tax charged are also shown in the report.
Inventory Overview
The Inventory includes the total amount of Stock in storage available for sale. The Unit Stock Management page will show the Inventory from where all Products with few different statuses i.e. Available, Broken, Reserved, Sold, Returned, or RMA allocated. So, by keeping track of the Inventory, the Shop Owner can manage different Product Stocks with different statuses for different types of Orders to compare Product stock versus Product sales.
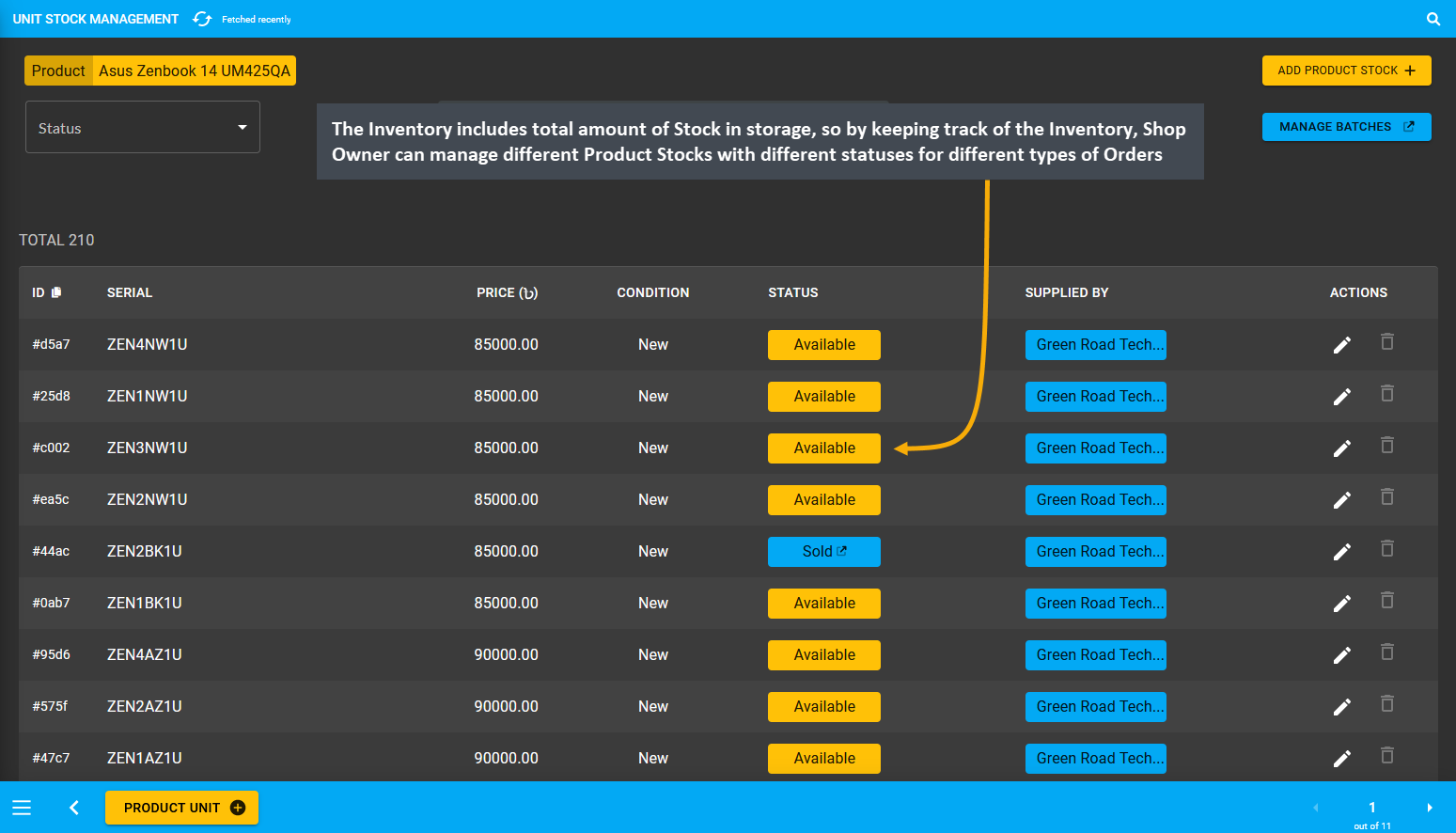
Image 9: The Inventory includes total amount of Stock in storage, so that Shop Owner can keep track of it.
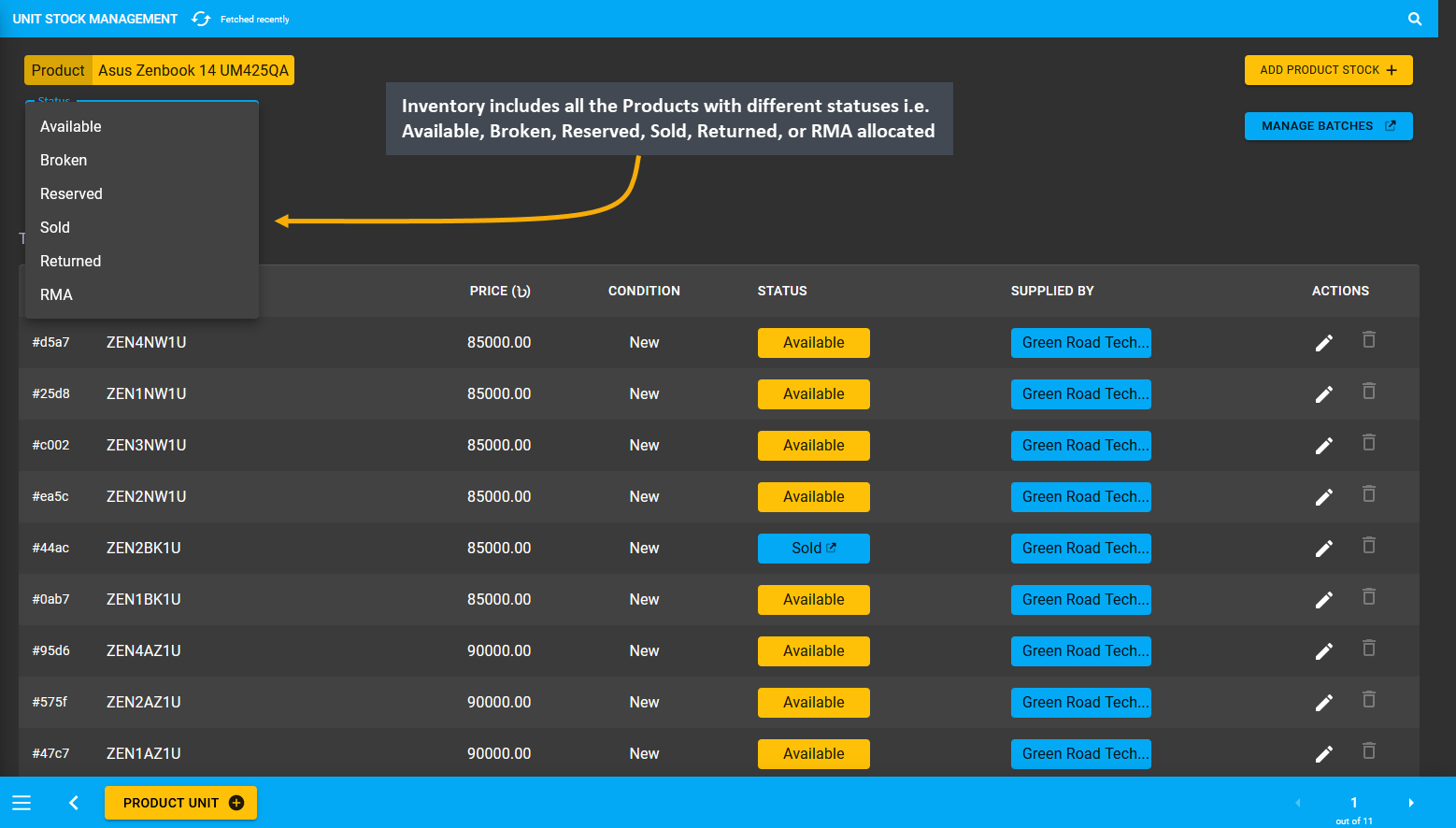
Image 10: Product inventory include Available, Broken, Reserved, Sold, Returned, or RMA allocated Products.
Create Return Policy for Customer
It is important for the Shop Owner to create a clear and concise Return Policy for Customers. Make sure that the Product Return Policy will give Customers a feeling of security in that the Products they will purchase is going to be exactly what they receive. Customers will always want to be guaranteed about the Products that they will be purchasing from the Shop Owner. So, create own Policy to add to the Website, or use our Return Policy template.
Establish a fair Return Policy for Customers which reflects the trust the Shop Owner have in the Products they sell. Create Return Policy with options for replacement Products, Ledger Credit, or Refund based on Customer’s claim.
Record Credit, Payable, and Receivable with Ledger
The Shop Owner needs to keep record of calculation between the business parties. For instance, the Shop Owner can calculate Payable, which means that that Credit Supplier will get the mentioned amount from Shop Owner. So, Payable is when something is purchased without paying right away. Selecting Payable for previous transaction on Import Ledger will add to Payable amount that the Shop Owner owes to the Credit Supplier.
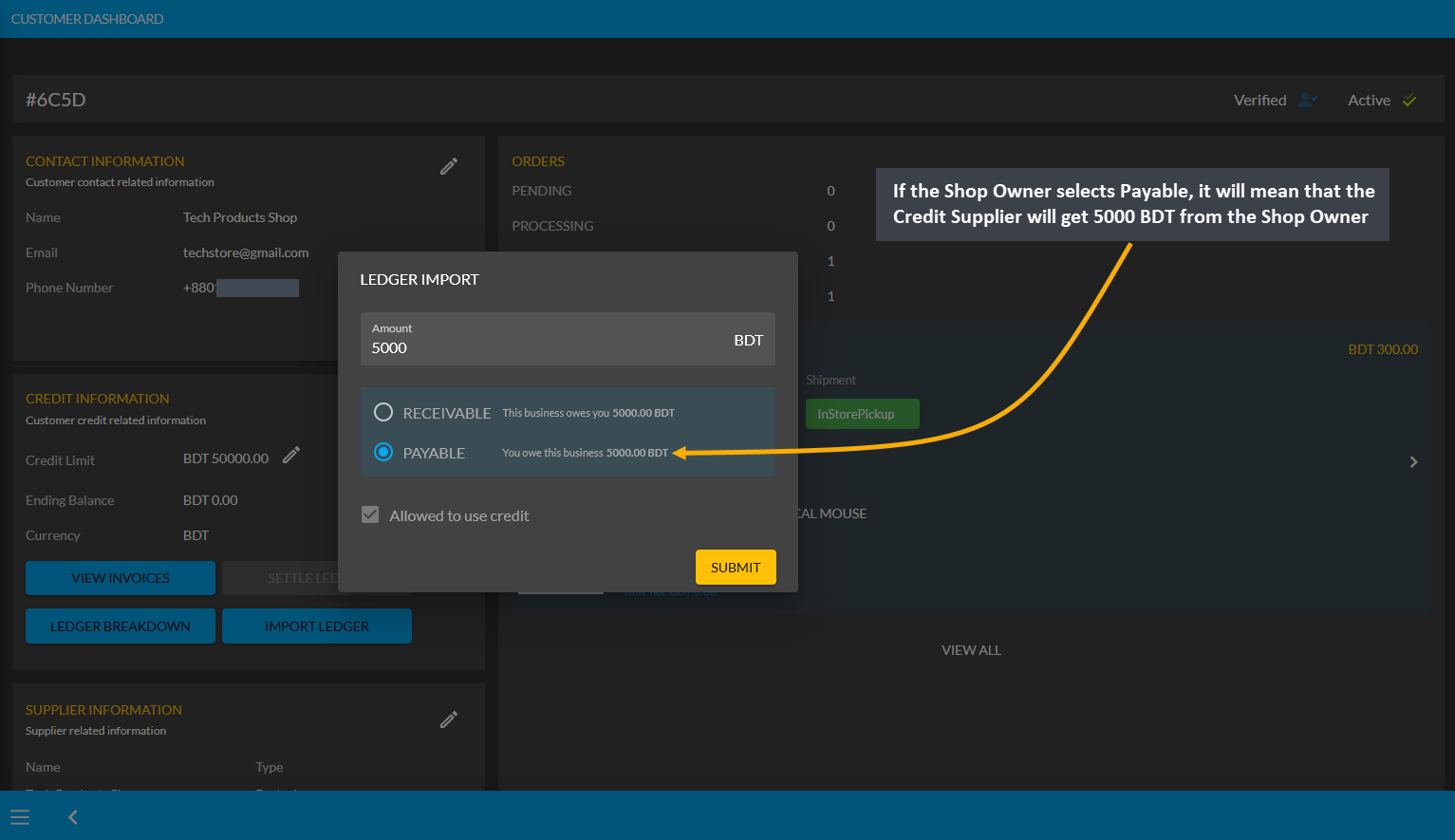
Image 11: If Shop Owner selects Payable, it means Credit Supplier will get mentioned amount from them.
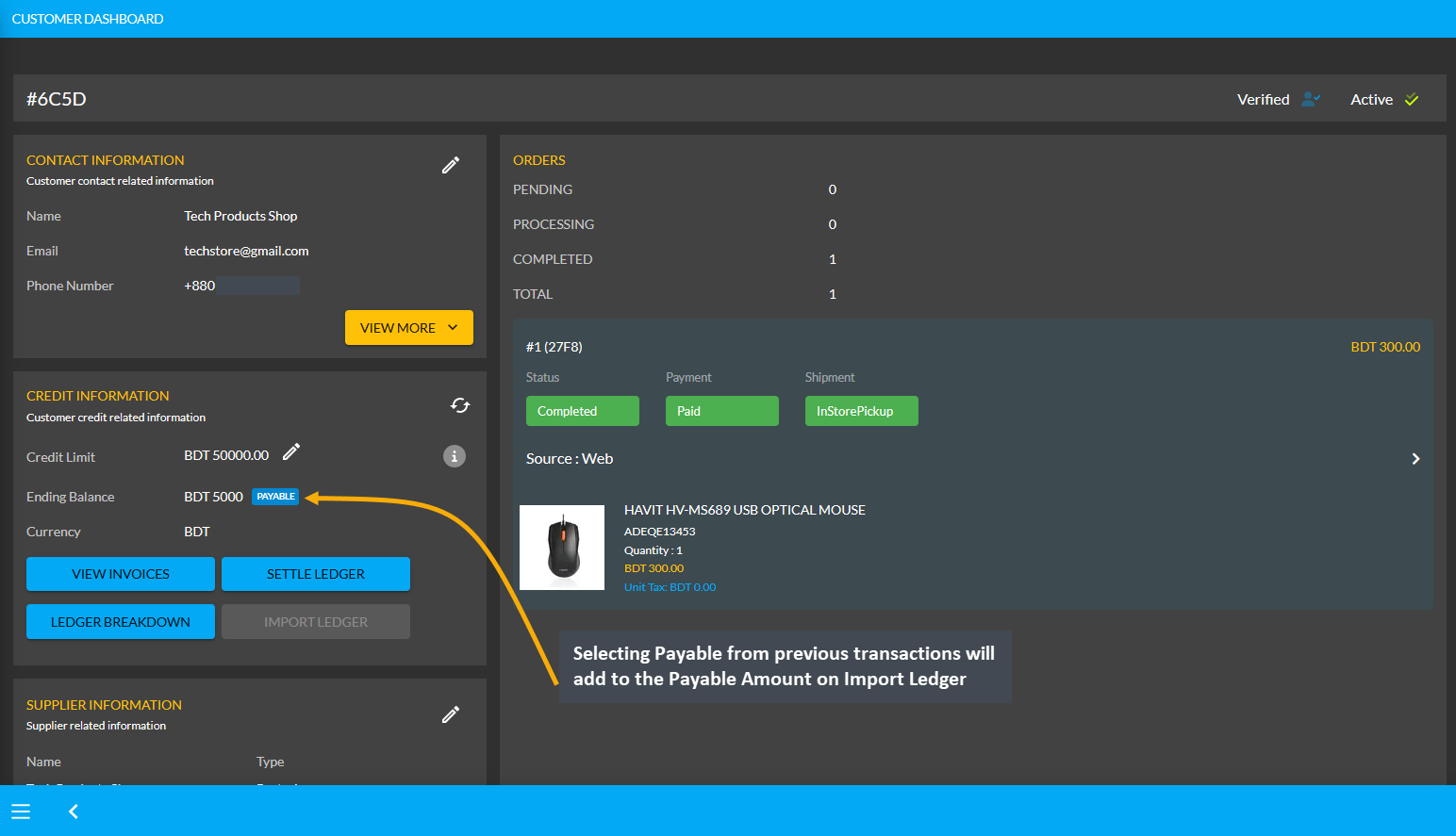
Image 12: Selecting Payable from previous transactions will add to the Payable Amount on Import Ledger.
Similarly, the Shop Owner can calculate Receivable, which means that the Credit Supplier will pay the mentioned amount to the Shop Owner. Thus, Receivable is when Shop Owner purchase something On Credit from the Credit Supplier. Selecting Receivable for previous transaction will add to the Receivable amount on Import Ledger which the Shop Owner owes from the Credit Supplier.
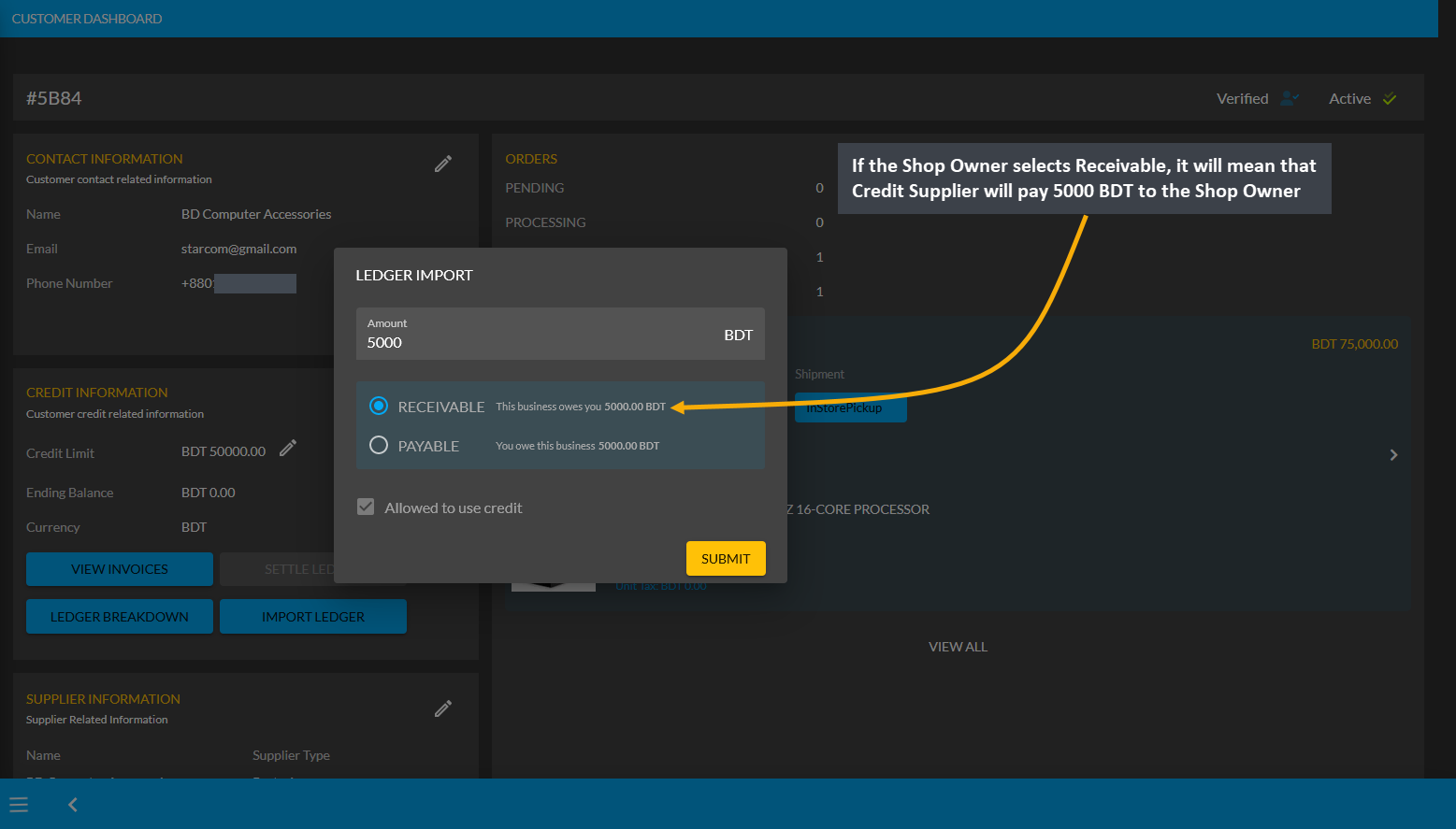
Image 13: If Shop Owner selects Receivable, it means Credit Supplier will pay mentioned amount to them.
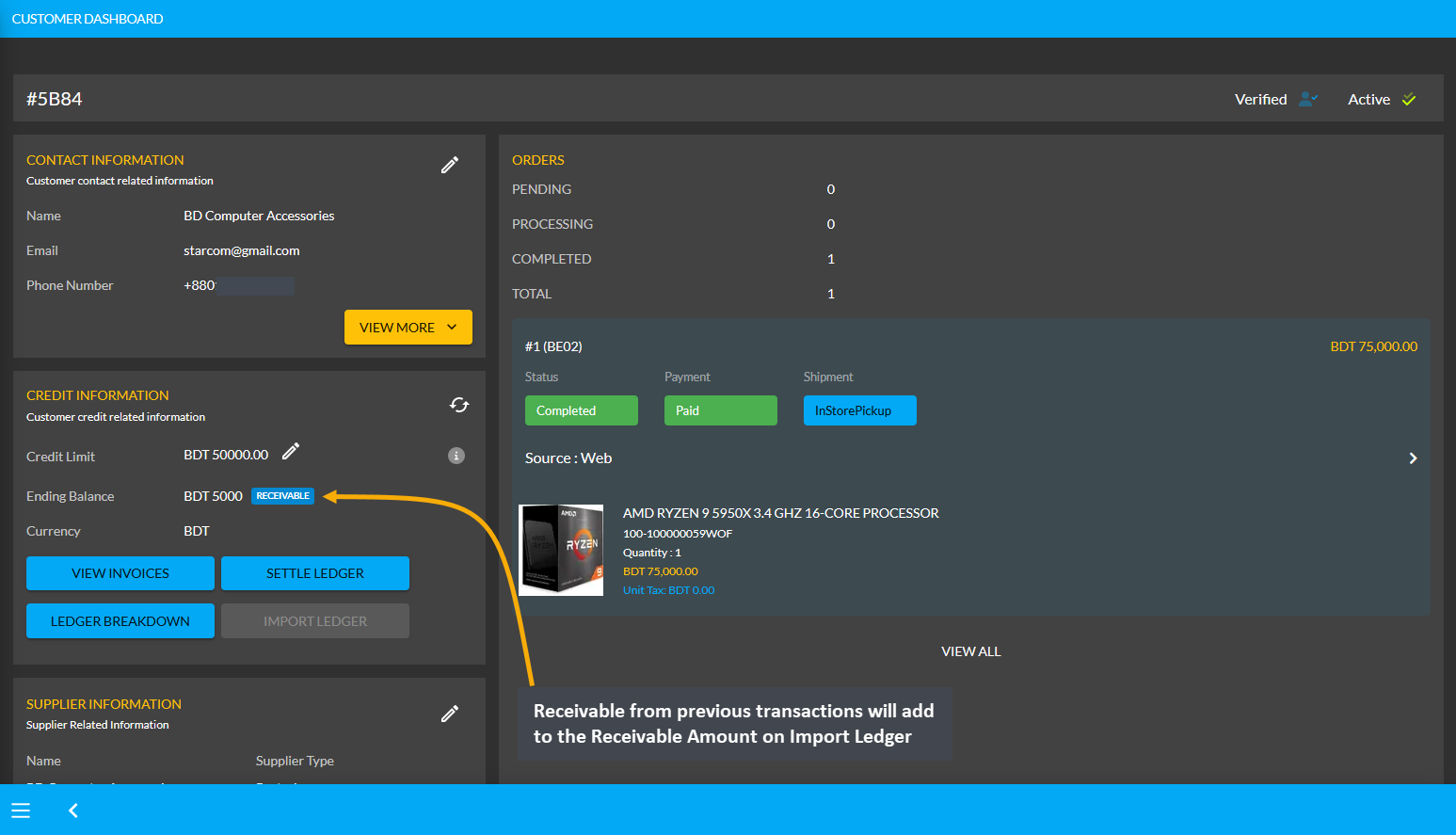
Image 14: Receivable from previous transactions will add to the Receivable Amount on Import Ledger.
The CMS has a Ledger system where Ledger is like a complete transaction history of day-to-day business. Shop Owners can decide to grant any Customer Credit Limit with which they can buy Products from the Shop Owner that will reflect in their Ledger. With Credit balance, Customers can purchase Products from Shop Owners using On Credit without having to instantly pay. All the transactions will be available on the Ledger Breakdown page.
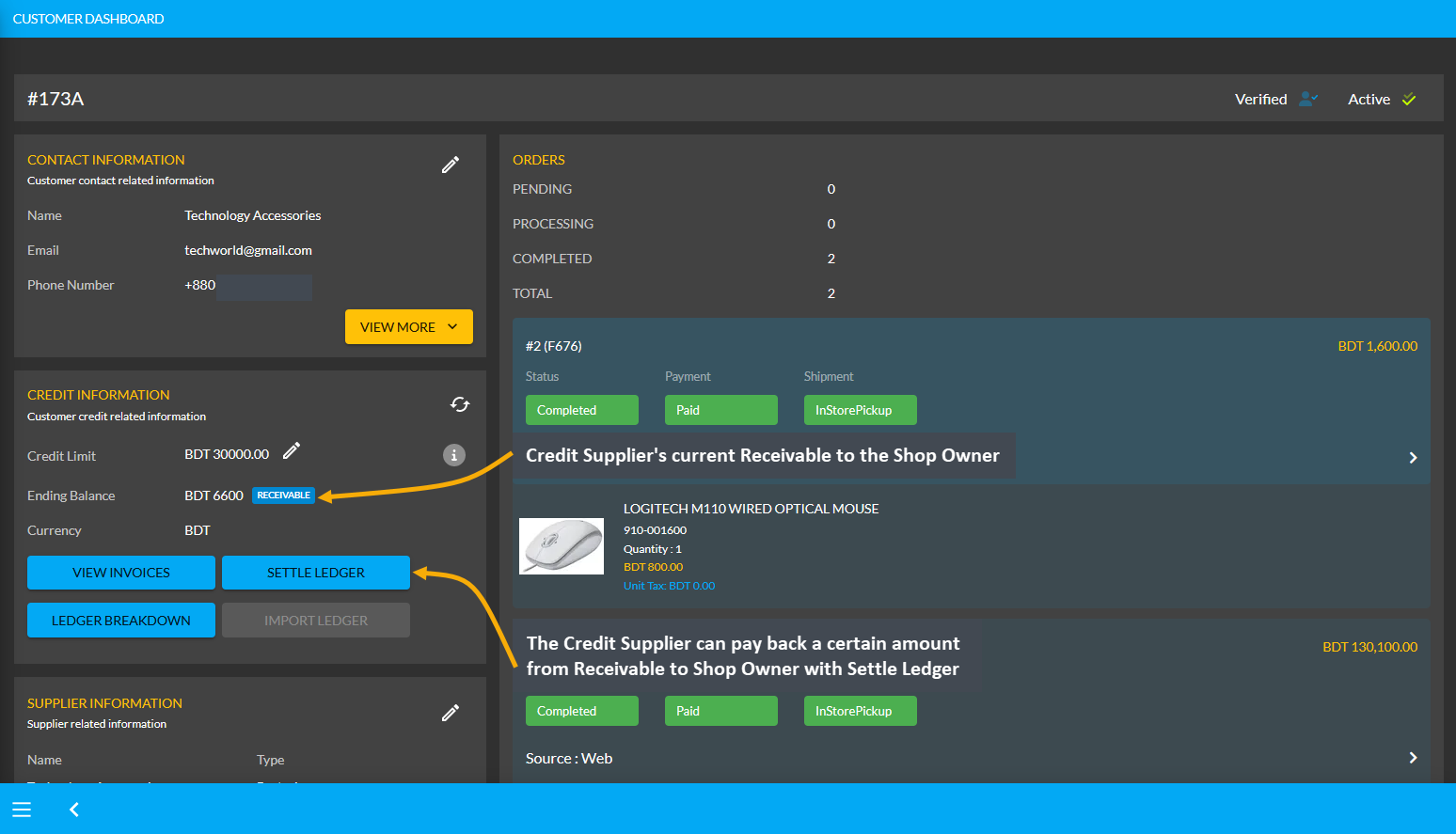
Image 15: Credit Supplier can pay back an amount from Receivable to Shop Owner with Settle Ledger feature.
Ledger balance can be settled with any Payment Gateway (Cheque, Cash On Delivery, Credit Card, SSLCommerz, Nagad, Nagad Manual, BKash Manual, BKash, PortWallet, Cash, and Bank Transfer) available within Settle Ledger.
Invoice with Payment History
Keep track of Payment history for the Website Orders through invoices for Customers as they make all Payments with Cash and other Payment Gateways, the details of which will be recorded. Verify all the payment information before approving transactions and avoid processing delays for both traditional and electronic payments. If Shop Owner need to check back on an old Order, they can refer back to invoices of those Orders from the Order List.
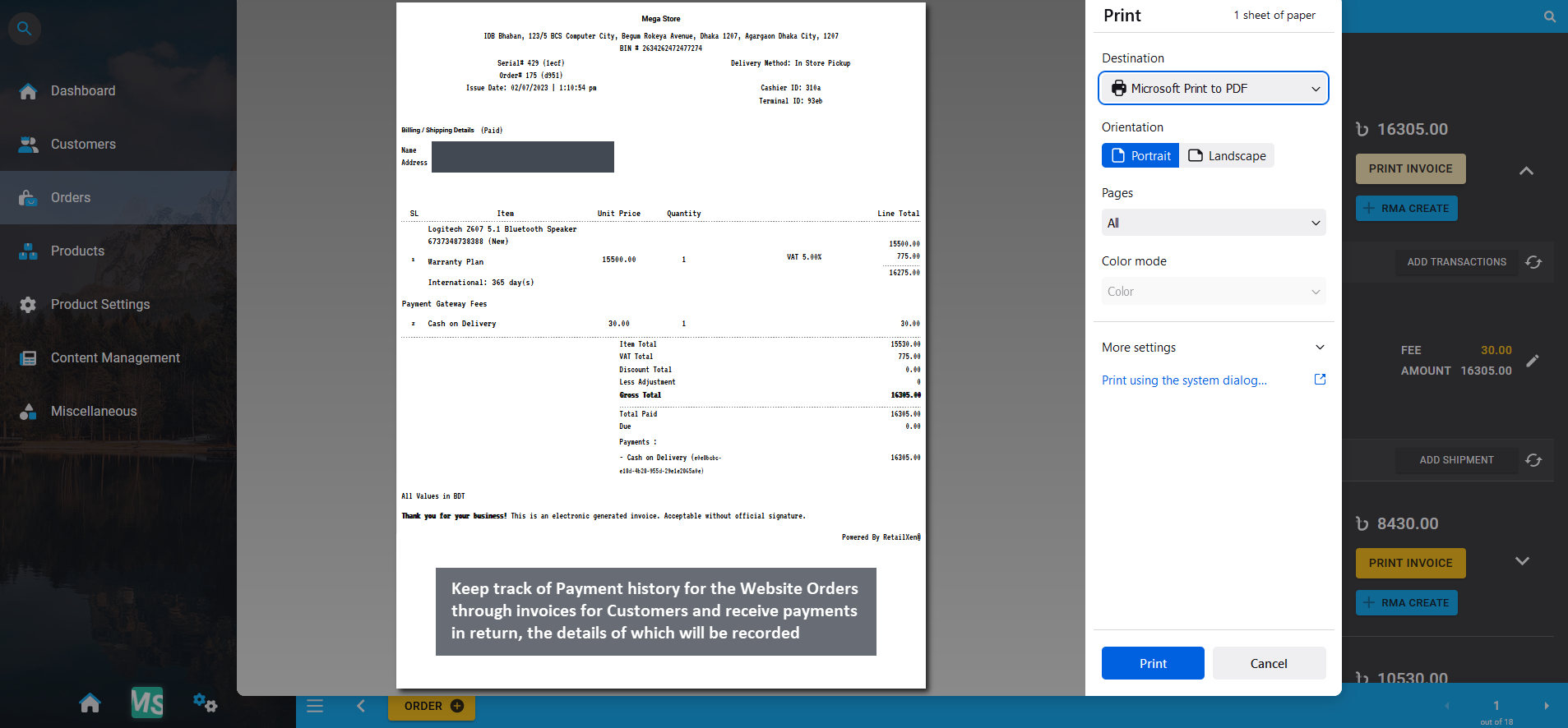
Image 16: Keep track of Payment history for the Website Orders through invoices for all type of Customers.
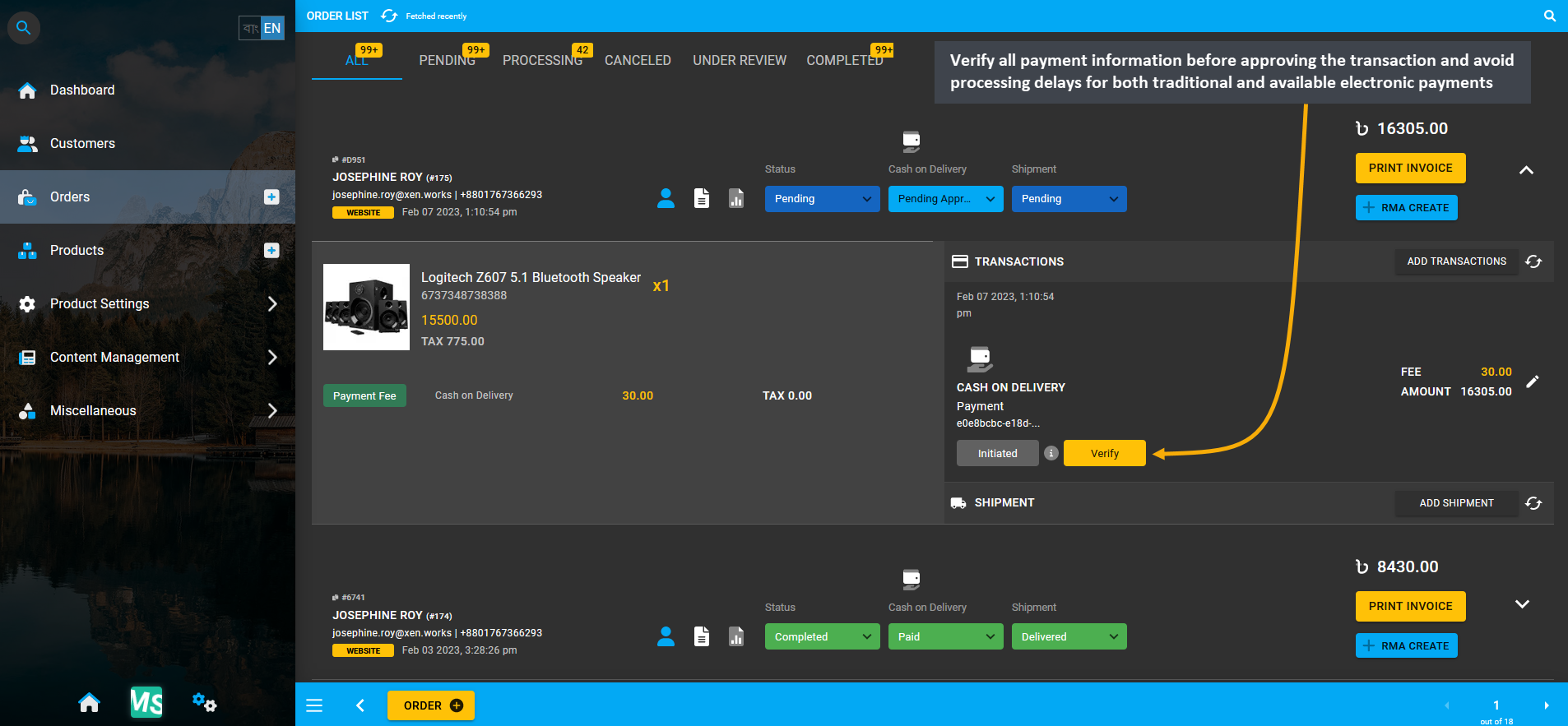
Image 17: Verify all the payment information before approving the transaction to avoid processing delays.
Create Terms for Service, Replacement, and Refund
The Shop Owner needs to create Terms for Service, Replacement, and Refund of Products. Customers can review these terms to file any claim on any Products quality issue if they are not satisfied with their purchase. The terms will apply to sales of all Products and the Customer can formally file a claim for warranty, service, replacement, or refund procedure. Refer to our Terms of Service and Return and Refund Policy templates to get clear ideas.
Create RMA Case to manage Product Claims
Retail Xen provides a Return Merchandise Authorization (RMA), through which Shop Owners can track all Product related claims, return process, warranty process, refund claims, custom service warranty, and Product exchange process. Using RMA workflow, the Shop Owners will be able to receive a Product, arrange exchange or refund, track warranties, and Product claims. Out of Warranty service can be provided by Shop Owners through RMA. Learn details of effective Warranty management by going through Return Merchandise Authorization (RMA).
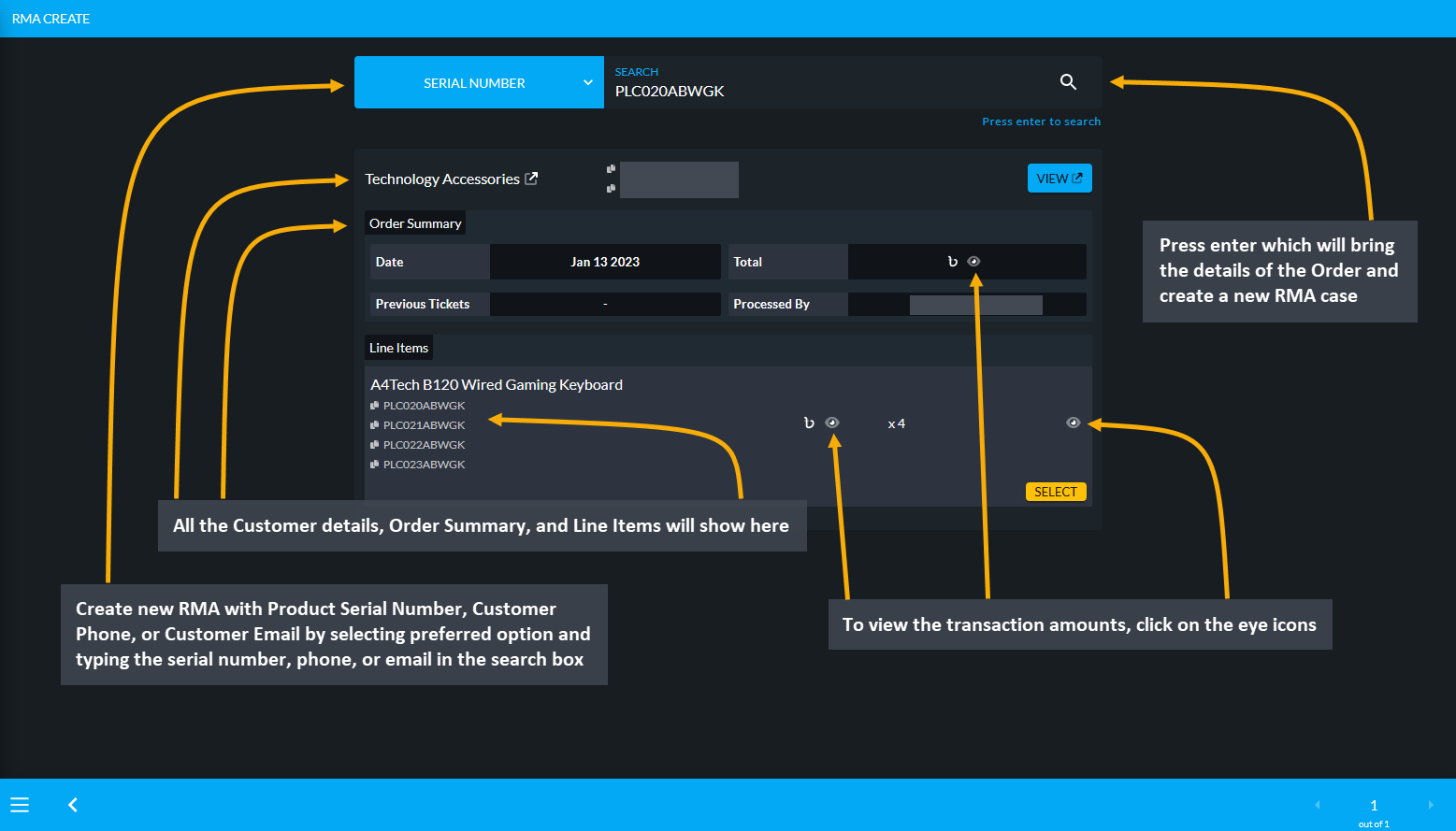
Image 18: Create new RMA with Product Serial Number, Customer Phone, or Customer Email by typing on search.
After RMA is created, the Order and RMA case details will show on the RMA View page. Within Product details, the purchased date, warranty date, sale price, and Related Cases will show. Below it are the RMA Workflow, which will allow Shop Owner to take action for the Product with different actions. There are several workflow actions such as Comment, Denial, Supplier, Service, Return, Exchange, Refund, and Warranty. Click on each of these workflows to add comment, upload images, and update status to save the workflow update for the RMA case.
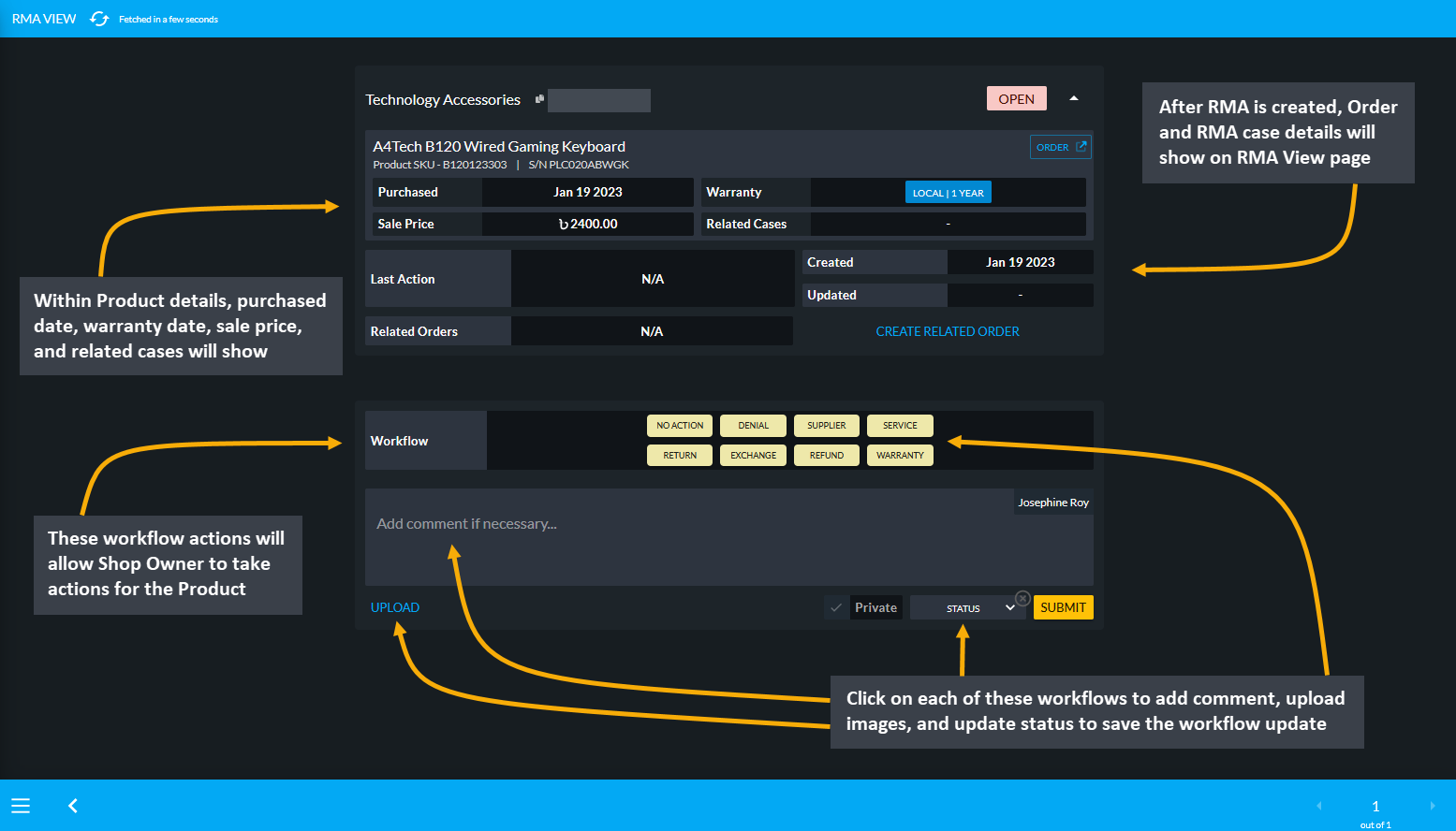
Image 19: Product details, Order details, RMA case details, RMA workflow actions and status can be updated.
Process After Warranty Service
Generally, After Warranty Service includes support, maintenance, and repair of Products purchased by Customer. They can request for technical or on-site support for after warranty service of Products from the Shop Owner. For instance, warranty for RMA case could include giving Product parts or service warranty. So, if warranty is expired, they can charge Customer regarding warranty related services, they can use the option to Create Related Orders.
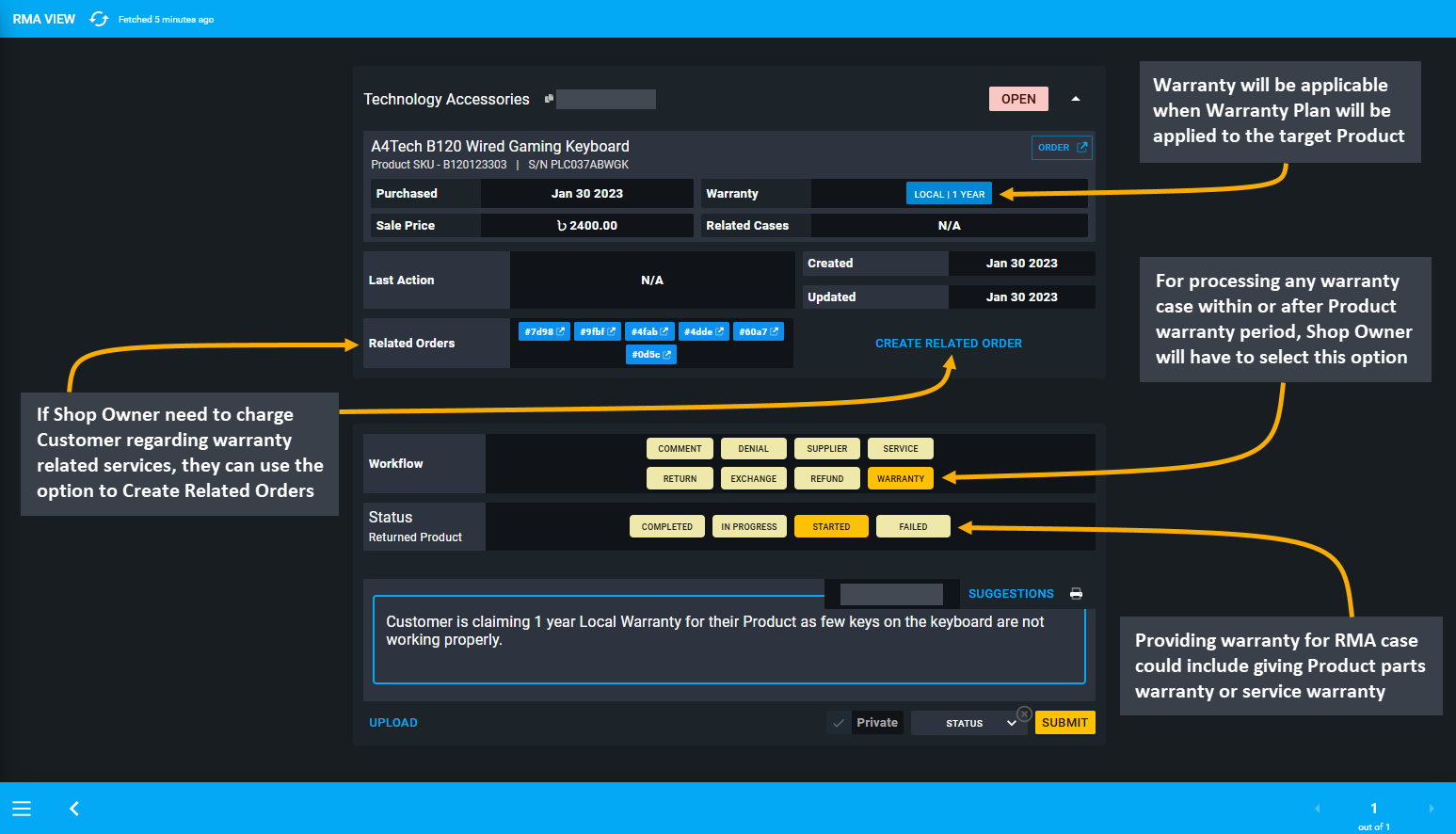
Image 20: Use Warranty to process any warranty case within or after Product warranty period that applies.